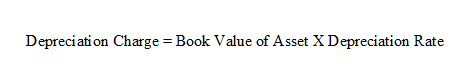Depreciation, Amortization, Depletion, and Impairment
Depreciation, amortization, depletion, and impairment are ways of accounting the using up or decline in value of long lived assets.
- Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of tangible assets to expense in a rational and systematic manner in the periods that the assets provide benefits.
- Amortization is the process of allocating the cost of intangible assets to expense in a rational and systematic manner in the periods that the assets provide benefits.
- Depletion is the process of recording the extraction of natural resources (wasting assets) to expense.
- Impairment is the process of recording the cost of an asset whose value lessoned to expense.
Three things needed to compute depreciation
- The depreciable base for the asset
- The asset’s useful life
- The depreciation method
Depreciable Base = Asset Cost – Salvage Value
Depreciation Methods
- Straight Line Method
- Activity Method
- Sum-of-the-Years'-digits Method
- Declining Balance Method
Straight Line Method
The straight-line method uniformly charges depreciation expense each of the asset’s service life
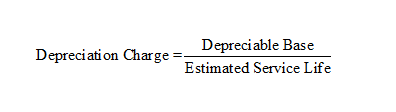
Activity Method
The activity method of deprecation is measure by a function of productivity. The depreciable base is multiplied by a ratio of the units of productivity divided by estimated total productivity. The units of productivity could be miles, produced units, hours.
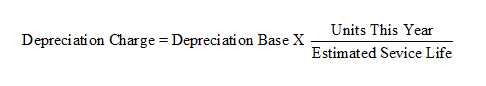
Sum-of-the-Digits Method
The Sum-of-the-Digits method is an accelerated depreciation method that heavily weighs depreciation to the early part of the assets life.
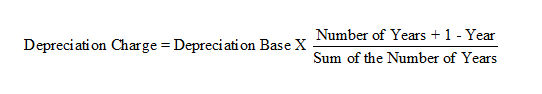
Declining-Balance Method
The declining-balance method is an accelerated depreciation method applies the same ratio each period to the current value of the asset, ignoring salvage value.
The percentage used is usual a multiple of straight-line depreciation rate.